People with dry skin conditions, such as eczema or dermatitis, psoriasis and ichthyosis, have an impaired skin barrier. Dry skin conditions can affect people of any ethnic origin and any age group from the very young to the elderly. Older people are prone to developing dry skin as the skin becomes thinner and less efficient at producing natural oils (sebum).
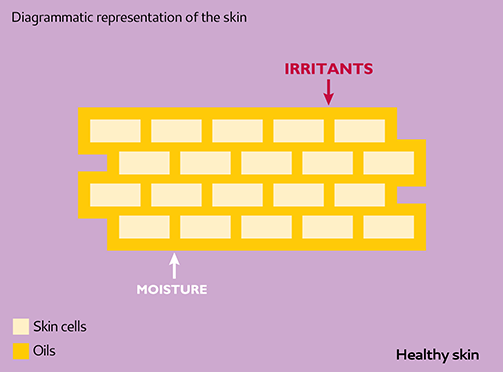
Healthy Skin
In healthy skin, natural oils fill spaces between plump skin cells of the outer layer to form a good skin barrier – keeping moisture in and irritants out.
The outer skin cells and the surrounding natural oils are often likened to a brick wall. The skin cells are the ‘bricks’ and the natural oils are the ‘mortar’.
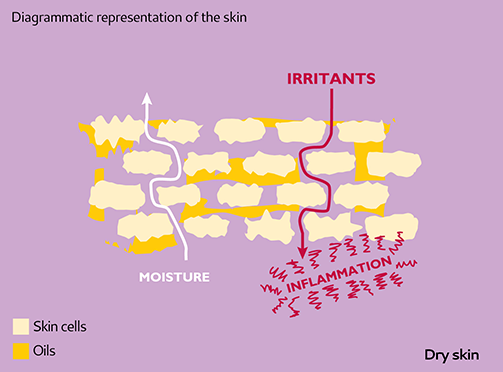
Dry skin – An impaired skin barrier
An impaired skin barrier has a shortage of natural oils which allows moisture to escape from the skin too quickly. The skin cells shrink, opening cracks which allow greater moisture loss and the entry of irritants. The skin then becomes dry and irritated, which can make it feel itchy.
Emollients, medical moisturisers, work by helping replace the missing oils which trap water into the skin and thus helping to restore the skin barrier and can also help with itch. People with medical dry skin conditions are often prescribed emollients. There are different types of emollients available and if you have a dry skin condition your GP, Nurse or Pharmacist may be able to prescribe an emollient that is most appropriate for you.